The installation of an underfloor heating system is not random; it requires precise planning and calculation to ensure optimal heating efficiency and energy efficiency. This article will discuss the method and steps of calculating the floor heating cable of a house in detail to help readers understand and implement this process.
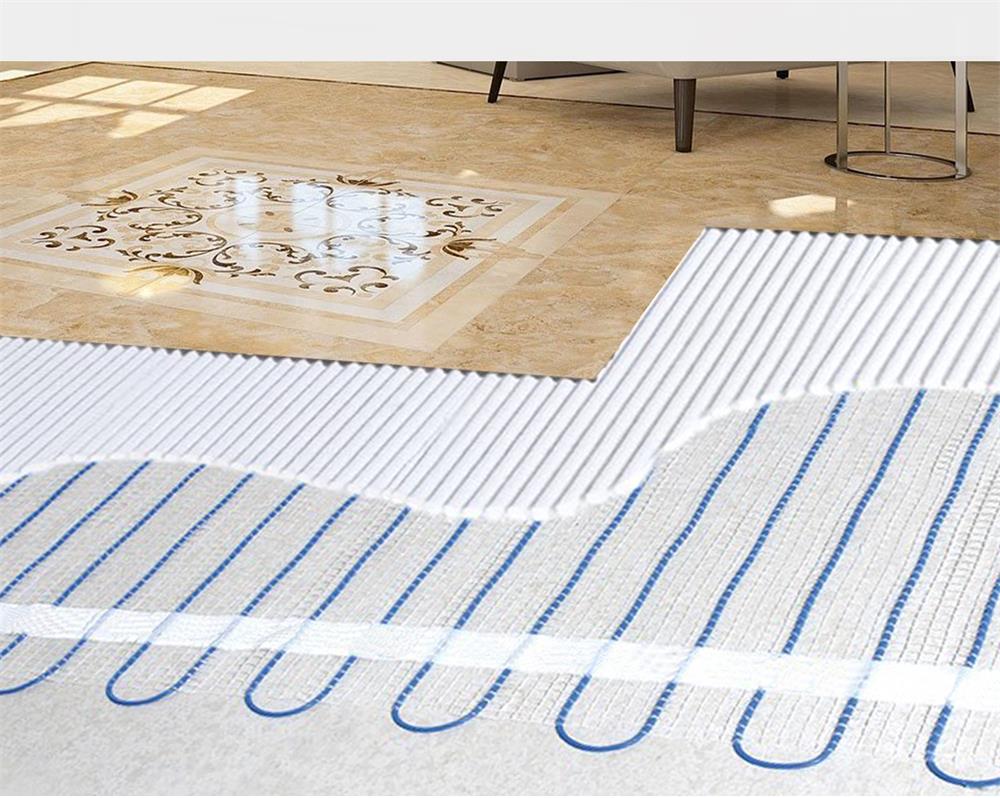
The core of the floor heating system lies in the laying of the floor heating cable. The laying density, layout and total length of the cable are directly related to the heating effect and energy consumption of the room. Therefore, calculating the number and layout of floor heating cables required for a room is a key step to ensure the performance of the floor heating system.
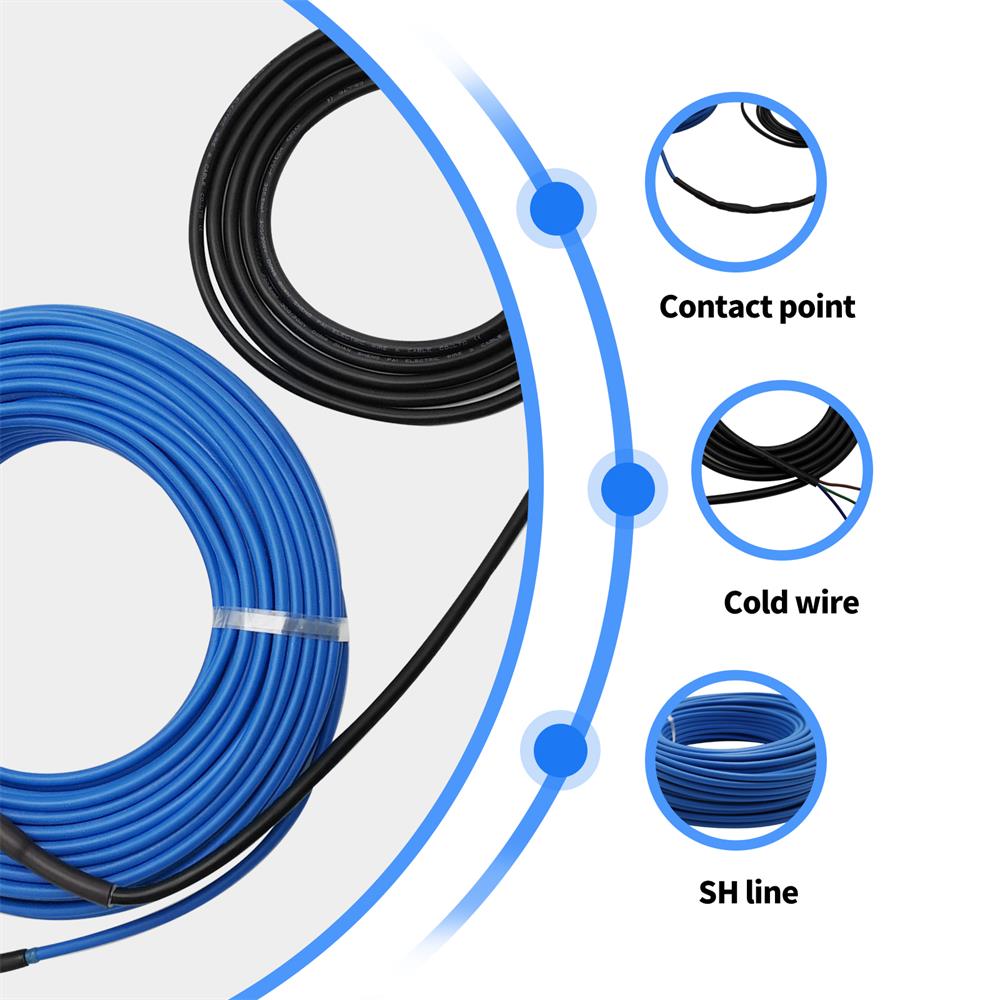
We need to understand the basic working principle and types of underfloor heating cables. Floor heating cables are usually divided into two types: single guide cables and double guide cables. Single-lead cables refer to cables with only one current loop, while double-lead cables have two current loops that can transmit heat in both directions. Two-guide cables are generally considered the better choice because of their higher thermal efficiency and more uniform heat distribution. However, the cost of the two-lead cable is also relatively higher.
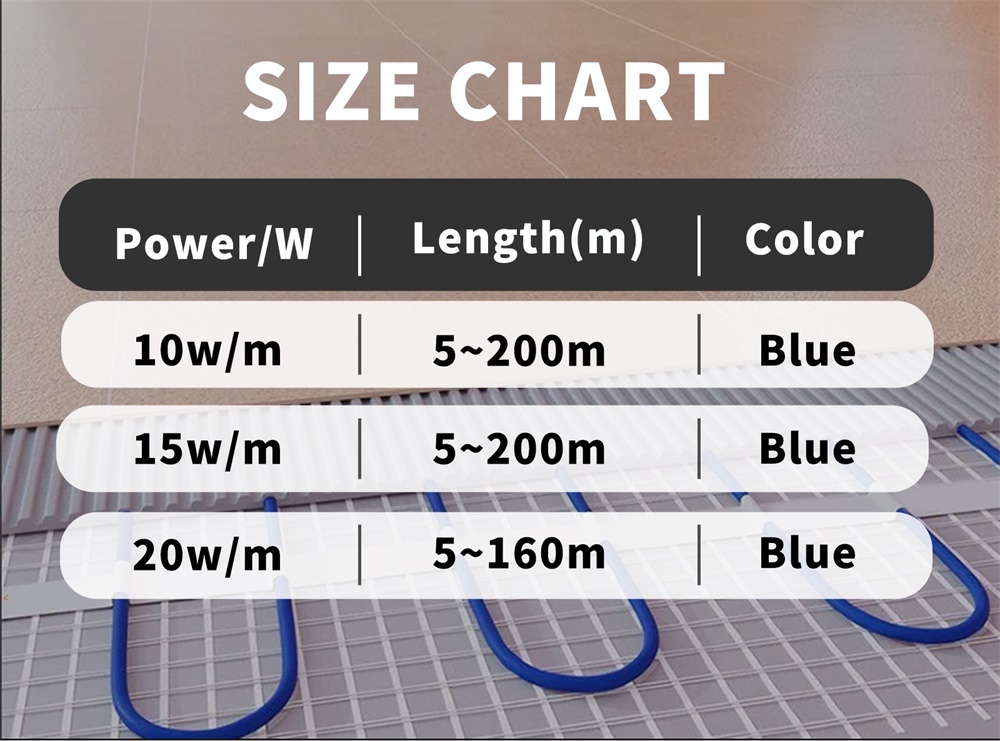
After determining the type of cable, the next step is to calculate the required cable length. This needs to be calculated based on the actual area of the room, the power of the selected cable, and the target room temperature. A common calculation method is to first measure the area of the room (square meters), and then determine the power required per square meter (watts/square meters) according to the selected cable specifications. For example, if the cable power selected is 100 watts/m2 and the room area is 20 m2, the total power required for the entire room is 2000 watts. Depending on the power of the cable, the required cable length can be calculated. If the power of a cable is 200 watts/meter, then 2000 watts requires 10 meters of cable.
However, the actual laying length of the cable also needs to take into account the laying mode. Common laying modes include serpentine laying and zigzag laying. Serpentine laying can save cable length, but may lead to uneven heat distribution; Although more cables are used in zigzag laying, the heat distribution is more uniform. In actual calculation, you need to adjust the cable length according to the laying mode.
In addition to the length and laying mode of the cable, other factors need to be considered, such as the thermal conductivity of the ground material, the thermal insulation performance of the room, etc. These factors all affect the efficiency of the underfloor heating system and the number of cables required. For example, if the ground material has poor thermal conductivity, it may be necessary to increase the laying density of the cable to ensure the heating effect.